Create Backend using Postgres + Express
- Siah Peih Wee

- Apr 7, 2022
- 4 min read
In this tutorial, you will learn how to write a simple backend using Postgres and Express. You may want to preview the code in my Github.

Setup Development Environment
ProjectName
-> backend
----> index.js
----> db.js
-> frontend
----> index.htmlInitialize NPM Package
Open "ProjectName" Folder in VSCode
Select "backend" folder > Right Click > Open in Integrated Terminal
Initialize NPM
npm initInstall Express & Postgres
npm i express
npm i pg
npm i cors
npm i dotenv
npm i nodemonexpress = Express
pg = Postgres
dotenv = Enviroment Variables
nodemon = Automatically Restart Node Application
Write Codes
Go to index.js in backend folder
Include Express and CORS Modules
Initialize Express and PORT number
Set Express app to show its running and listen to PORT
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INCLUDES
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors');
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INIT
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// DISPLAY SERVER RUNNING
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
app.get('/',(req,res)=> {
res.send(`Server running on port ${PORT}`)
});
app.listen(PORT,()=> {
console.log(`App listening to port ${PORT}`);
});Edit package.json
Look for package.json in backend folder
Edit the scripts to
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./index.js",
"dev": "nodemon /index.js"
}Run Server
Start the server by doing the following in Integrated Terminal
npm startYou should see the following log message in console or terminal
App listening to port 3000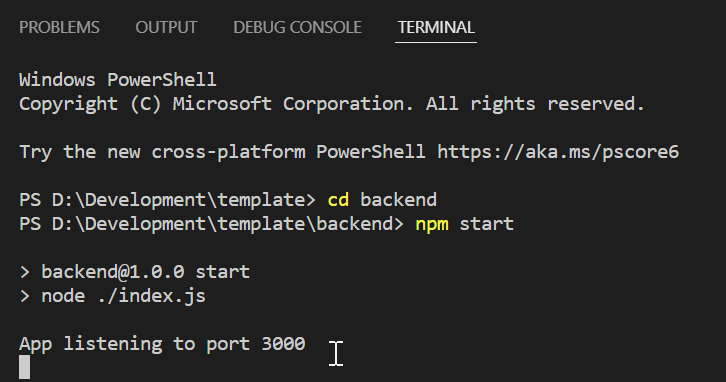
Open Browser > Go to the URL ---> http://localhost:3000
You should see the body of the document showing
Server running on port 3000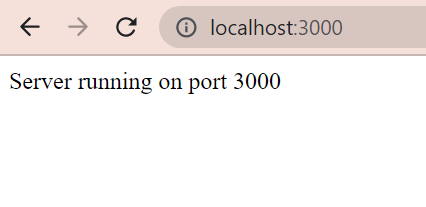
Install Postman
Type in URL in Text Field beside the word GET
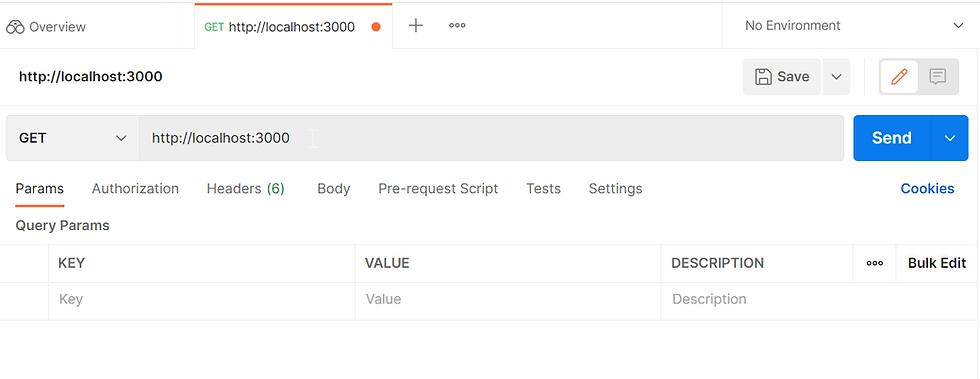
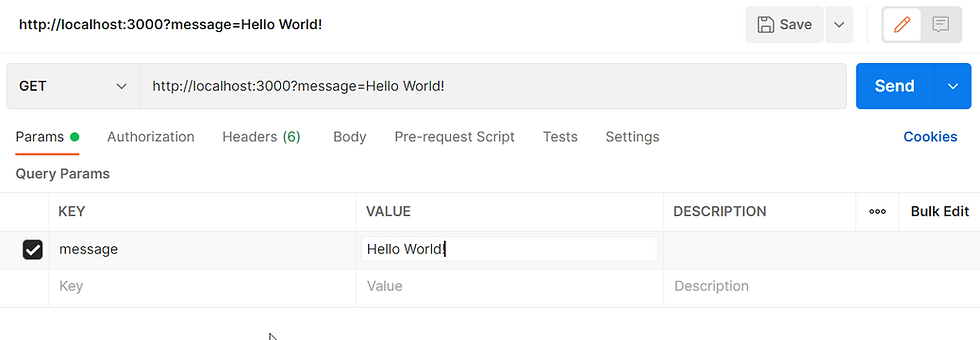
GET Request with Postman
For GET, use Params and set the Key and Value
POST Request with Postman
You can use raw JSON [ Recommended ]
For POST, use Body > raw
Then set the Key and Value in JSON formats
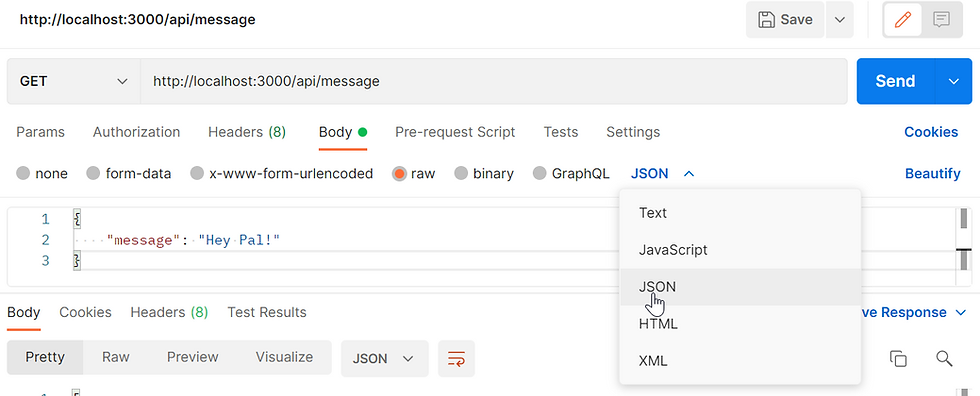
or
For POST, use Body > x-www-form-urlencoded
Then set the Key and Value
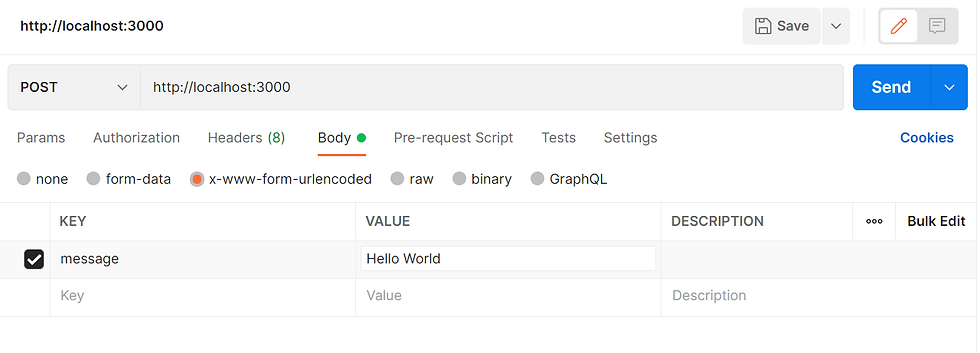
Setup Express App
Setup to use CORS
Setup to use JSON
Setup to parse URLEncoded payload
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SETUP APP
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
app.use(cors());
app.use(express.json());
// REQUIRED TO READ POST>BODY
// If not req.body is empty
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false}));POST and GET Methods in Express
Create both POST and GET methods
req is Request
res is Response
Set the Routing Path to "/api"
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// POST GET METHODS
// http://localhost:3000/api/
// Use Postman to test
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
app.get('/api', async (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.query);
res.json(req.query);
});
app.post('/api', async (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.body);
res.json(req.body);
});Test POST in Express
Type in the Key and Value, press Send
You should see the response body.
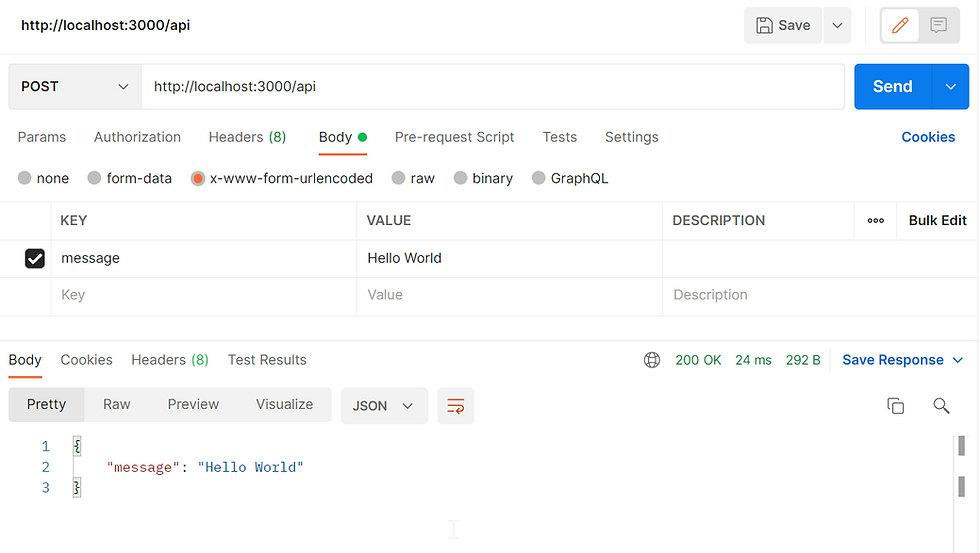
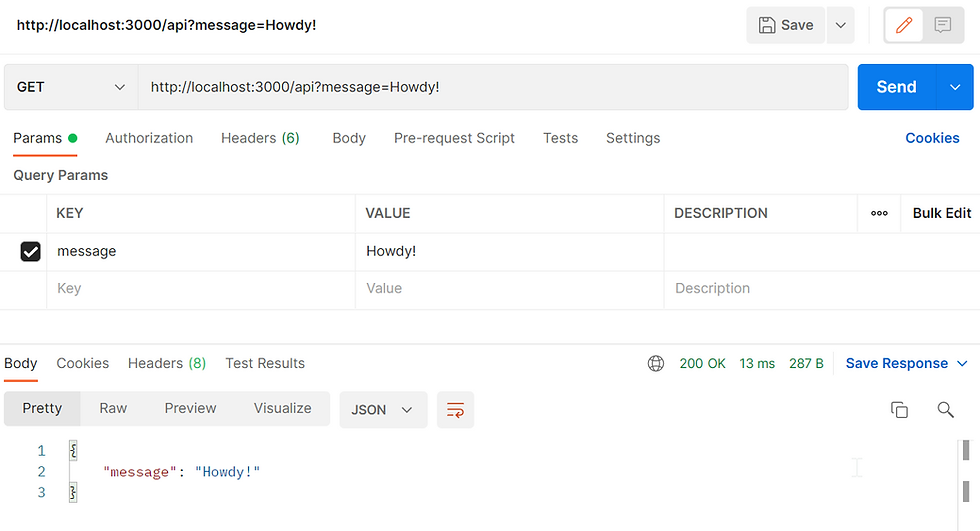
Test GET in Express
Type in the Key and Value, press Send
You should see the response body.
Setup Postgres DB Instance
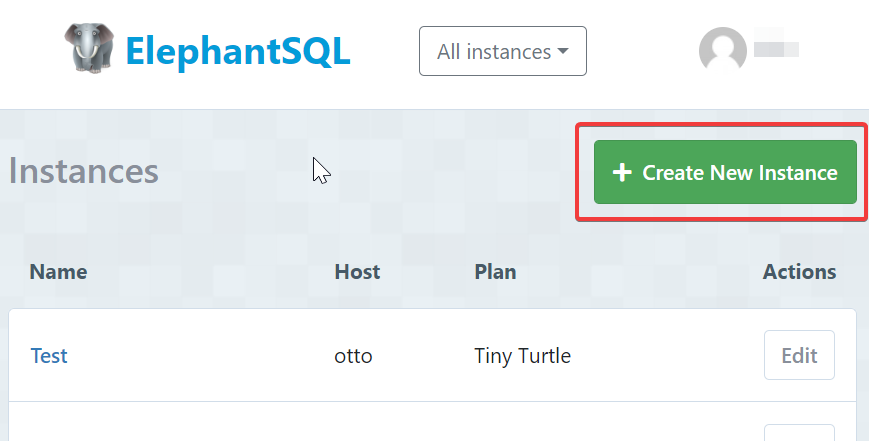
Go to ElephantSQL
Register an account
Click on Create New Instance
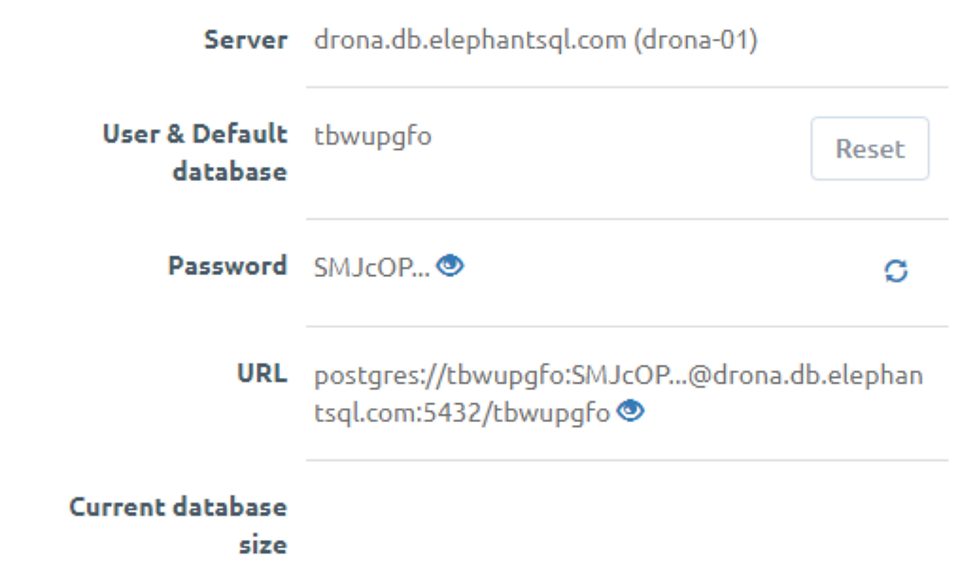
Create Environment Variables File
Copy the URL from your ElephantSQL instance
Select .env file to edit
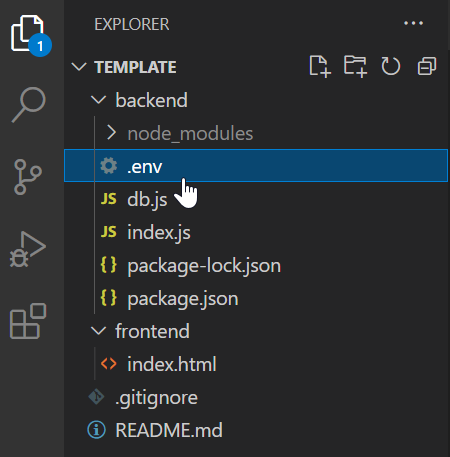
Add DATABASE_URL, paste the URL you copied from your ElephantSQL as the value.
DATABASE_URL=postgres://YourUserName:YourPassword@localHost:5432/YourDatabaseNameSetup DB Connection
Go to db.js in backend folder
Include Enviroment Variables (dotenv) module
Include Postgres (pg) module
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INCLUDES
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/* Include to use .env file */
require('dotenv').config();
const pg = require('pg');
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// DATABASE_URL extracted from .env file
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const dbConfig = { connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL };
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CONNECTION TO DB
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const pool = new pg.Pool({
...dbConfig,
max: process.env.MAX_CONNECTION || 5,
});
module.exports = pool;Include DB Module
Go to index.js in backend folder
Include the module from db.js to use the Postgres Pool
const pool = require('./db'); //Import from db.jsCreate Table
Create a constant variable CREATE_TABLE_SQL to store the SQL statement
Set the Routing Path to "/api/create_table"
Use the Pool to query using the SQL statement
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SETUP DB
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const CREATE_TABLE_SQL = `
CREATE TABLE messages (
id SERIAL primary key,
message VARCHAR not null
);
`;
app.post('/api/table', async (req, res, next) => {
pool.query(CREATE_TABLE_SQL)
.then(() => {
res.send(`Table created`);
})
.catch((error) => {
res.send(error);
});
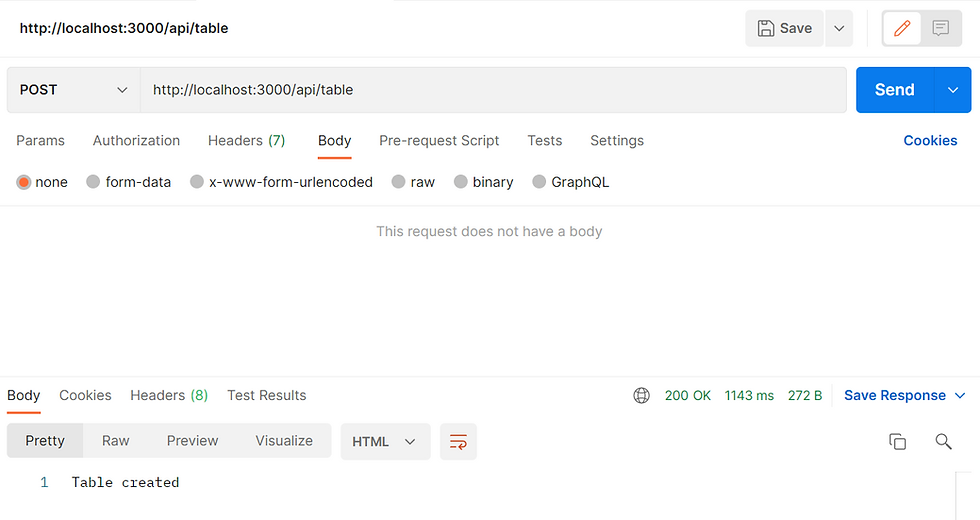
});Test in Postman to create the table using http://localhost:3000/api/table by POST
The response will show "Table created"
If the table was created previously, it will show error.
Drop Table
Create a constant variable DROP_TABLE_SQL to store the SQL statement
Set the Routing Path to "/api/drop_table"
Use the Pool to query using the SQL statement
NOTE: This is important if you want to try create the table again.
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CLEAR DB
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const DROP_TABLE_SQL = `
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS messages;
`;
app.delete('/api/table', async (req, res, next) => {
pool.query(DROP_TABLE_SQL)
.then(() => {
res.send(`Table dropped`);
})
.catch((error) => {
res.send(error);
});
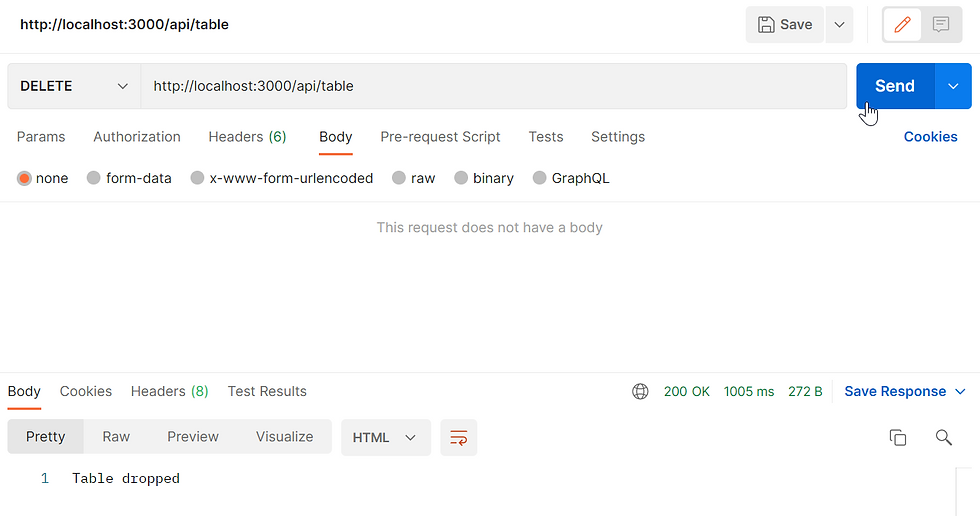
});Test in Postman to create the table using http://localhost:3000/api/table by DELETE
The response will show "Table dropped"
Add Routing Path to INSERT and SELECT
Create a constant variable DROP_TABLE_SQL to store the SQL statement
Set the Routing Path to "/api/message"
Use the GET to do SELECT, this is to get all messages in Table
Use the POST to do INSERT, this is to add new message into Table
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// POST GET METHODS CONNECTED TO DB
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
app.get('/api/message', async (req, res, next) => {
try
{
console.log(req.query);
const allMessage = await pool.query("SELECT * FROM messages");
res.json(allMessage.rows);
}
catch(err)
{
console.error(err.message);
}
});
app.post('/api/message', async (req, res, next) => {
try
{
console.log(req.body);
let message = req.body.message;
const newInsert = await pool.query("INSERT INTO messages (message) VALUES ($1) RETURNING *", [message]);
res.json(newInsert);
}
catch(err)
{
console.error(err.message);
}
});Test POST in Postman
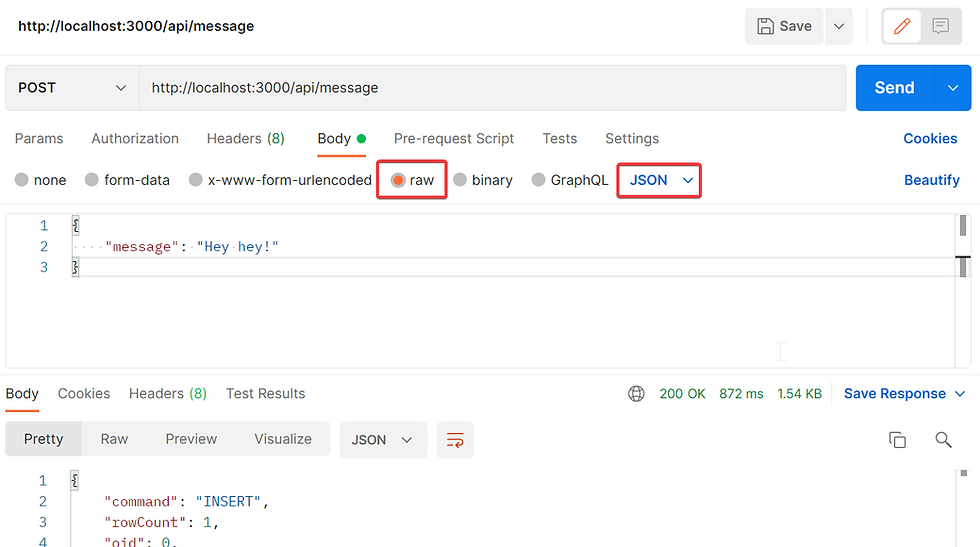
Method 1 (Recommended)
Using raw & JSON
Using the POST, set the Body to { "message" : "Any message you preferred" } .
Once Send, you should see the response.
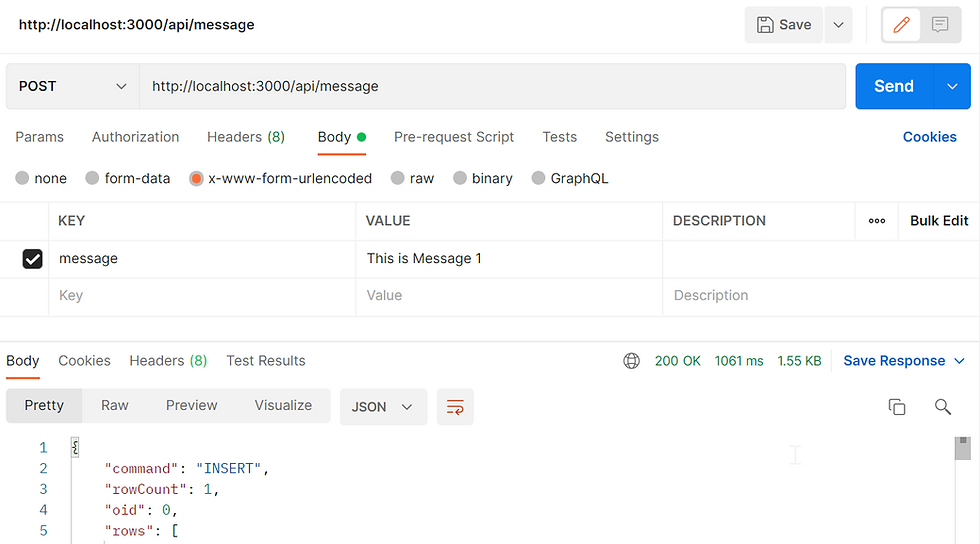
Method 2
Using the POST, set the Key to "message" and Value to "Any message you preferred".
Once Send, you should see the response.
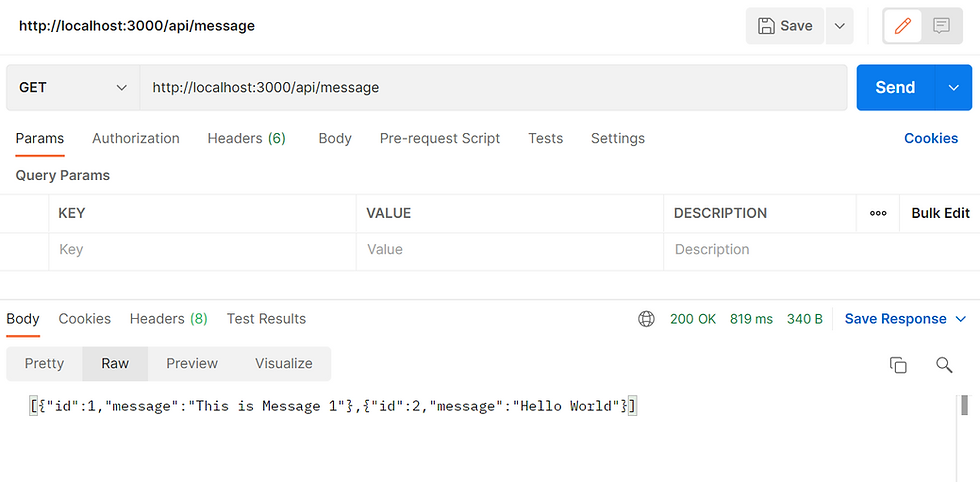
Test GET in Postman
Using the GET, without any Params.
Once click on Send, you should see the response.
You should see all the previous inserts.


Comments